Python 150 Interview Questions and Answers for Fresher in 2025
Are you a fresher preparing for a Python interview in 2025? To help you succeed, myLearnnest Training Institute has compiled a collection of 150 Python interview questions and answers for freshers, carefully gathered from real interview experiences at top MNC companies.
This resource is designed to give beginners a strong foundation in Python and the confidence to face technical interviews. The questions cover a wide range of essential topics including Python basics, data types, control structures, functions, OOP concepts, file handling, exception handling, libraries, and frameworks. In addition, we’ve included scenario-based questions to test your problem-solving and coding abilities, which are crucial for real-world projects.
Unlike generic question banks, our MNC-sourced content reflects the latest industry interview trends, ensuring you are preparing with authentic and relevant material. Each answer is explained in a clear, beginner-friendly manner, so even freshers can understand the concepts and apply them effectively.
Whether you’re targeting your first job as a Python Developer, Software Engineer, or Data Analyst, these 150 interview questions and answers will help you prepare smarter and stand out in interviews. With myLearnnest’s expert-curated resource, you can confidently take the next step toward launching your career in Python programming.
Python Training in Hyderabad – MyLearnNest Training Academy
At MyLearnNest Training Academy, we provide the best Python Training in Hyderabad, designed to equip learners with the most in-demand programming skills for today’s IT industry. Our job-oriented Python course covers everything from fundamentals to advanced concepts, including data types, control structures, OOPs, exception handling, file handling, modules, libraries, frameworks (Django, Flask), and best coding practices.
Students gain hands-on experience through real-time projects, coding challenges, and dedicated lab sessions, enabling them to develop applications, automate tasks, and work on data-driven projects. The training also includes exposure to industry-relevant tools and technologies like Pandas, NumPy, and SQL integration, preparing learners for real-world programming and data analytics challenges.
Whether you’re a fresher starting your career or an IT professional looking to upskill, MyLearnNest offers flexible learning options such as classroom training, online classes, and self-paced modules. We provide 100% placement assistance with resume building, mock interviews, and interview preparation to help students secure roles like Python Developer, Software Engineer, Data Analyst, or AI/ML Engineer.
With expert trainers, lifetime course access, and continuous mentoring, MyLearnNest ensures learners gain strong coding expertise and the confidence to excel in technical interviews. Enroll today in our Python Training in Hyderabad and take your first step toward a rewarding career in programming and data science.

150 Python Interview Questions and Answers for Fresher in 2025 Collected from TOP MNCs
- What is Python?
Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability. It supports multiple programming paradigms and has a large standard library. Python is widely used in web development, automation, data science, and more.
- What are the key features of Python?
Python is easy to learn, open-source, and dynamically typed. It supports object-oriented and functional programming and has vast libraries for various tasks. Its syntax is clean, which makes coding faster and easier.
- What is the difference between list and tuple in Python?
Lists are mutable, meaning you can change their contents, whereas tuples are immutable. Lists use square brackets [ ] and tuples use parentheses ( ). Tuples are generally faster and used for fixed data.
- How is Python interpreted?
Python code is executed line-by-line by the Python interpreter. It converts the source code into bytecode and then executes it using the Python Virtual Machine. This makes Python an interpreted language.
- What are Python’s data types?
Python has several built-in data types like int, float, str, list, tuple, dict, set, and bool. These types help store different kinds of data in variables. You can also define custom data types using classes.
- What is PEP 8?
PEP 8 is the official style guide for Python code. It defines how Python code should be formatted to improve readability. It covers naming conventions, indentation, line length, and more.
- What are Python functions?
Functions in Python are reusable blocks of code that perform specific tasks. They are defined using the def keyword and can take arguments and return values. Functions help make code modular and easier to maintain.
- What is the difference between is and == in Python?
The == operator checks if two variables have the same value, while is checks if they refer to the same object in memory. For example, a == b may be True, but a is b might be False. Use is for identity comparison and == for value comparison.
- What is indentation in Python?
Indentation in Python is used to define blocks of code. Unlike other languages that use braces {}, Python uses whitespace. Incorrect indentation leads to syntax errors.
- What are Python keywords?
Keywords are reserved words in Python that have special meaning and cannot be used as variable names. Examples include if, else, for, while, class, and def. There are around 35 keywords in Python.
- How do you write comments in Python?
Single-line comments start with a # symbol, and multi-line comments can be written using triple quotes ”’ or “””. Comments help explain the code and are ignored by the interpreter. They’re useful for code documentation.
- What is a variable in Python?
A variable is a name used to store data in memory. In Python, you don’t need to declare the type of variable explicitly. The type is inferred from the value assigned to it.
- What is type conversion in Python? Type conversion is the process of changing one data type to another, like int to float or str to int. Python supports implicit and explicit type conversion. Functions like int(), float(), and str() are used for this.
- What are Python loops?
Python supports for and while loops to perform repetitive tasks. for loops iterate over a sequence, while while loops continue as long as a condition is true. Loops can be controlled using break and continue.
- What is the difference between break and continue?
break exits the loop completely, while continue skips the current iteration and moves to the next one. Both are used to control the flow inside loops. They’re useful for optimizing loop behavior.
- What are Python strings?
Strings are sequences of characters enclosed in quotes. They are immutable, meaning their content cannot be changed. Python provides many methods to manipulate strings like upper(), lower(), and replace().
- How do you handle exceptions in Python?
Python uses try, except blocks to handle exceptions and prevent program crashes. You can also use finally for cleanup actions. This makes error handling smoother and more controlled.
- What is a dictionary in Python?
A dictionary is a collection of key-value pairs enclosed in {}. Keys must be unique and immutable, while values can be of any type. It’s used to store data in a structured and fast-access format.
- What is a module in Python?
A module is a file containing Python code such as functions, variables, and classes. You can import it into other programs using the import statement. Python has many built-in modules like math and random.
- What is the difference between local and global variables?
A local variable is defined inside a function and is accessible only within that function. A global variable is declared outside functions and is accessible throughout the program. You can use the global keyword to modify a global variable inside a function.
- What is a class in Python?
A class is a blueprint for creating objects. It defines attributes and behaviors (methods) common to all objects of that type. You define a class using the class keyword.
- What is an object in Python?
An object is an instance of a class with its own data and functions. Objects are created from classes using the class constructor. They help organize code using object-oriented programming.
- What is inheritance in Python?
Inheritance is a feature that allows one class (child) to inherit properties and methods from another class (parent). It promotes code reuse and improves maintainability. Python supports single and multiple inheritance.
- What is the use of self in Python?
self refers to the instance of the class and is used to access variables and methods of the current object. It must be the first parameter in instance methods. It helps differentiate between class variables and local variables.
- What are Python lambda functions?
Lambda functions are anonymous functions defined using the lambda keyword. They can have any number of arguments but only one expression. They’re often used for short, throwaway functions.
- What is recursion in Python?
Recursion is a function calling itself to solve a smaller part of the problem. It continues until a base condition is met. Python allows recursion but has a recursion limit to prevent infinite loops.
- What is the difference between append() and extend() in Python lists?
append() adds a single element to the end of the list, while extend() adds all elements from another iterable. append() adds the whole object, extend() adds individual elements. Both modify the original list.
- What are Python sets?
A set is an unordered collection of unique items in Python, defined with curly braces {}. It doesn’t allow duplicates and supports mathematical operations like union and intersection. Sets are useful for filtering and comparing data.
- What is the purpose of the pass statement in Python?
The pass statement does nothing and is used as a placeholder. It’s useful when a statement is required syntactically but you don’t want any code to run. It avoids syntax errors in empty code blocks.
- How do you create a virtual environment in Python?
You can create a virtual environment using the python -m venv env_name command. It isolates project dependencies from the system Python installation. Activate it with source env_name/bin/activate or env_name\Scripts\activate.
- What is the use of the with statement in Python?
The with statement simplifies resource management like opening and closing files. It ensures that resources are properly released, even if an error occurs. It is commonly used with file operations.
- What is slicing in Python?
Slicing lets you extract parts of a sequence like lists, strings, or tuples. It uses the syntax sequence[start:stop:step]. It helps retrieve sub-parts without modifying the original data.
- What is the difference between remove() and pop() in lists?
remove() deletes the first matching value, while pop() removes the item at a specific index and returns it. remove() does not return anything, but pop() does. Both modify the original list.
- What is the purpose of id() in Python?
The id() function returns the unique identifier of an object, which corresponds to its memory address. It helps check if two variables point to the same object. It’s useful for debugging and identity checks.
- What are mutable and immutable data types in Python?
Mutable types like lists and dictionaries can be changed after creation. Immutable types like strings, tuples, and integers cannot be changed. Choosing the right type depends on whether data should be modifiable.
- What is list comprehension?
List comprehension is a concise way to create lists using a single line of code. It uses a loop and optional condition inside square brackets. It improves readability and performance.
- How do you install packages in Python?
You use the pip command, like pip install package_name, to install Python packages. It fetches and installs packages from the Python Package Index (PyPI). Pip is the standard package manager for Python.
- What is the purpose of __init__() method in classes?
The __init__() method is the constructor in Python classes. It runs automatically when a new object is created and is used to initialize attributes. It helps set up objects with initial data.
- What is a Python iterator?
An iterator is an object that allows you to loop over a sequence one element at a time. It implements __iter__() and __next__() methods. You can create custom iterators in classes too.
- What is the difference between == and != in Python?
== checks if two values are equal, and != checks if they are not equal. These are comparison operators used in conditional statements. They return Boolean values: True or False.
- How do you handle multiple exceptions in Python?
You can handle multiple exceptions using multiple except blocks or by grouping them in a tuple. This ensures specific or general errors are caught appropriately. It helps make code more robust.
- What is the use of range() in Python?
The range() function generates a sequence of numbers and is often used in loops. It can take 1 to 3 arguments: start, stop, and step. It returns a range object, which is memory efficient.
- What is the purpose of the dir() function?
dir() returns a list of all valid attributes of an object. It’s useful for introspection and debugging. It helps you discover the methods and variables available for any object.
- What are Python decorators?
Decorators are functions that modify the behavior of other functions or methods. They are applied using the @decorator_name syntax. Decorators are commonly used for logging, authorization, and caching.
- What is a Python generator?
Generators are functions that yield values one at a time using the yield keyword. They are memory-efficient because they don’t store all items in memory. You iterate through them like lists.
46. What are *args and kwargs in Python?
*args allows a function to accept any number of positional arguments, and **kwargs accepts any number of keyword arguments. They help create flexible functions. Both are useful in advanced function definitions.
- What is the use of enumerate() in Python?
enumerate() adds a counter to an iterable and returns it as an enumerate object. It’s useful when you need both index and value in a loop. It enhances readability and performance.
- What is the difference between isinstance() and type()?
type() returns the exact type of an object, while isinstance() checks if an object is of a specified type or its subclass. isinstance() is more flexible and recommended for type checking.
- What is the use of zip() in Python?
zip() combines elements from multiple iterables into tuples. It’s useful for parallel iteration over two or more sequences. The result is an iterator of tuples.
- What is the purpose of map() in Python?
map() applies a function to all items in an iterable and returns a map object. It allows for functional-style processing of sequences. It’s often used with lambda for compact code.
- What is the difference between filter() and map() in Python?
map() applies a function to all elements of an iterable, while filter() returns elements that match a condition. filter() keeps only the items for which the function returns True. Both return iterators.
- What is docstring in Python?
A docstring is a special string written inside triple quotes right after defining a function, class, or module. It describes what the function or module does. You can access it using the __doc__ attribute.
- What is the difference between return and print() in Python?
print() displays the result on the screen, while return sends the result back to the caller. return is used to pass data out of functions. print() is used mainly for debugging or user output.
- What is the purpose of globals() and locals()?
globals() returns a dictionary of global variables, while locals() returns a dictionary of local variables. They are useful for introspection and debugging. You can also use them to dynamically access variables.
- What is a namespace in Python?
A namespace is a container that holds variable names and their values. Python has different namespaces: local, global, and built-in. It helps avoid name conflicts and manages scope. - What are Python’s built-in data structures?
Python has four main built-in data structures: lists, tuples, sets, and dictionaries. Each has unique characteristics for storing and manipulating data. They’re the foundation for handling collections. - What is a shallow copy vs. deep copy?
A shallow copy creates a new object but references the same inner objects, while a deep copy creates new inner objects too. Use copy() for shallow and deepcopy() from copy module for deep. Deep copy ensures full duplication.
- What is the use of del in Python?
The del keyword is used to delete variables, list items, or dictionary entries. It frees memory by removing references. It can also delete slices in lists.
- What is the purpose of __name__ == “__main__” in Python?
It checks whether a Python script is being run directly or imported as a module. If it’s run directly, the block inside runs. It helps control code execution.
- How do you read a file in Python?
You use the open() function with mode ‘r’ to read a file. Then, use .read(), .readline(), or .readlines() to get content. Always close the file using .close() or a with statement.

- How do you write to a file in Python?
Use open() with mode ‘w’ or ‘a’ to write or append to a file. Then use .write() or .writelines() methods. Always close the file or use with to auto-close.
- What is the difference between open(‘file.txt’, ‘w’) and open(‘file.txt’, ‘a’)?
‘w’ opens the file for writing and overwrites existing content, while ‘a’ appends content to the end. Both create the file if it doesn’t exist. Use ‘a’ to preserve old data.
- What is a Python package?
A package is a directory containing Python modules and a special __init__.py file. It allows you to organize related modules together. Packages help structure large projects. - What are Python libraries?
Libraries are collections of pre-written code that provide specific functionality. Python has many built-in and third-party libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib. Libraries make development faster and easier.
- What is try-except-finally block in Python?
It’s used for exception handling: try runs the code, except catches exceptions, and finally runs cleanup code regardless of success or error. It ensures proper resource handling.
- What is an assertion in Python?
An assertion is a debugging aid that tests a condition using the assert keyword. If the condition is False, it raises an AssertionError. It’s used to catch bugs early.
- How is memory managed in Python?
Python manages memory using reference counting and a garbage collector. When an object’s reference count drops to zero, it gets deleted. The garbage collector handles cyclic references.
- What is a Python compiled file?
A compiled Python file has a .pyc extension and contains bytecode, not source code. It’s created automatically when a module is imported. It speeds up loading in future runs.
- What is monkey patching in Python?
Monkey patching means dynamically modifying or extending code at runtime. You can change class or module behavior without changing its source. It’s powerful but should be used carefully. - What are Python magic methods?
Magic methods start and end with double underscores, like __init__, __str__, and __len__. They let you define special behaviors for your classes. They are also called dunder methods. - What is the use of super() in Python?
super() is used to call methods from a parent class. It’s commonly used in inheritance to extend functionality. It avoids hardcoding the parent class name.
- What is a metaclass in Python?
A metaclass is a class of a class that defines how classes behave. You use it to control class creation. It’s an advanced feature not commonly needed in basic programming.
- What is the purpose of repr() in Python?
repr() returns a string that represents the object in a way that can be used to recreate it. It’s mainly for debugging and development. It complements the str() function.
- What is the difference between int() and float()?
int() converts a value to an integer, dropping any decimal part. float() converts a value to a floating-point number with decimals. They are used for numeric type conversions.
- What is the use of the any() and all() functions?
any() returns True if at least one element in an iterable is True, while all() returns True only if all are True. They’re useful for quick condition checks on lists or tuples.
- What is the re module in Python?
The re module provides support for regular expressions. It lets you search, match, and replace patterns in strings. It’s useful for text processing and validation.
- What is the use of lambda in Python?
A lambda is an anonymous function defined with the lambda keyword. It can take any number of arguments but only one expression. It’s useful for short, throwaway functions.
- What is the use of split() and join()?
split() breaks a string into a list using a separator, while join() combines a list into a string with a separator. They are helpful in string manipulation. Both are commonly used for data formatting.
- What are escape characters in Python?
Escape characters allow you to include special characters in strings, like \n for newline or \t for tab. They start with a backslash. They’re useful in formatting output.
- What is string interpolation in Python?
String interpolation means inserting values into strings. It can be done using f-strings (f”{name}”), format(), or % formatting. F-strings are the most modern and readable way.
- What are binary, octal, and hexadecimal literals in Python?
Python supports binary (0b), octal (0o), and hexadecimal (0x) number literals. They represent values in different number systems. You can convert between them using built-in functions.
- What is the use of typecasting in Python?
Typecasting converts a variable from one type to another, like from int to float. It’s done using functions like int(), str(), float(). It helps in data processing and calculations.
- What is the difference between input() and raw_input()?
In Python 3, input() reads a string from the user. raw_input() was used in Python 2 for the same purpose. In Python 3, raw_input() no longer exists.
- What are logical operators in Python?
Logical operators are and, or, and not. They are used to combine conditional statements. They return Boolean values based on the logic.
- What is indentation in Python?
Indentation refers to spaces at the beginning of a line to define code blocks. It replaces braces like {} in other languages. Proper indentation is critical for Python code to run correctly.
- What is the use of the is keyword?
The is keyword checks for identity, meaning if two variables refer to the same object in memory. It is different from ==, which checks for value equality. It’s used for object comparisons.
- What is the difference between continue and break?
break exits the loop completely, while continue skips the current iteration and moves to the next one. Both control the loop flow. They are used inside loops for conditions.
- What is None in Python?
None is a special constant in Python representing the absence of a value. It’s commonly used as a default argument or return type. It is not the same as 0, False, or an empty string.
- What is the difference between a method and a function?
A function is a block of code defined using def, while a method is a function that belongs to an object. Methods are called on objects using dot notation. Functions can be standalone or part of a class.
- What is a ternary operator in Python?
A ternary operator is a one-line if-else statement: value_if_true if condition else value_if_false. It simplifies conditional expressions. It’s good for quick decisions.
- How do you reverse a list in Python?
You can reverse a list using list.reverse() or slicing like list[::-1]. reverse() changes the list in place. Slicing creates a new reversed list.
- What are Python keywords?
Keywords are reserved words that have special meaning in Python, like if, else, while, class. You can’t use them as variable names. Python has about 35 keywords.
- How do you find the length of a list or string?
Use the built-in len() function to find the length of lists, strings, and other collections. It returns the number of elements. It’s a simple and commonly used function.
- What is a Python tuple?
A tuple is an immutable sequence of values. It’s defined using parentheses like (1, 2, 3). You can’t modify its contents after creation.
- How is a dictionary different from a list?
A dictionary stores key-value pairs and is unordered, while a list stores ordered values with integer indexes. Dictionaries use curly braces and keys. Lists use square brackets and indexes.
- What is the difference between count() and index() in lists?
count() returns how many times an element appears in the list. index() returns the position of the first occurrence. Both are list methods used for searching.
- What is unpacking in Python?
Unpacking allows you to assign multiple variables in one line using a sequence. Example: a, b = [1, 2]. It’s useful for returning multiple values from functions.
- What is the purpose of zip(*iterables)?
zip() groups elements from multiple iterables, and zip(*iterables) unzips or reverses that grouping. It’s used for transposing data structures. It’s handy for pairing and unpairing data.
- What is the difference between == and is in Python?
== checks for value equality, while is checks for object identity. Two different objects with the same value are == but not is. It’s important when comparing objects.
- What is the use of format() method in strings?
The format() method inserts values into placeholders in strings. It uses {} to define placeholders. It’s a flexible way to build dynamic strings.
- What are Python decorators?
Decorators are functions that modify the behavior of other functions. They are applied using the @decorator_name syntax above a function. They’re commonly used for logging, authentication, and performance tracking.
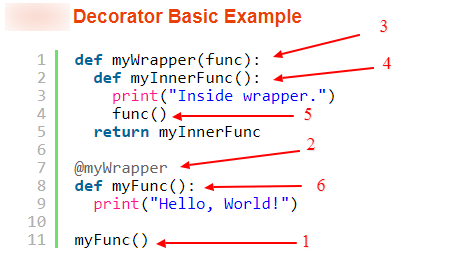
- What is the purpose of enumerate()?
enumerate() adds a counter to an iterable and returns it as an enumerate object. It’s useful when you need both the index and the value in a loop. It simplifies looping over items with positions.
- What is the use of pass in Python?
pass is a placeholder that does nothing when executed. It’s used where code is syntactically required but you don’t want any action. It’s common in function or loop stubs.
- What is a Python iterator?
An iterator is an object with a __next__() method that returns items one by one. It remembers its state during iteration. Iterators are used in loops and comprehensions.
- What is a Python generator?
A generator is a function that yields values one at a time using the yield keyword. It returns an iterator and saves memory. It’s great for large data streams.
- What is the difference between yield and return?
return ends a function and sends back a value, while yield pauses the function and returns a value. A function with yield becomes a generator. yield allows resuming from the same point.
- What is the use of the with statement?
The with statement is used to wrap the execution of a block with methods defined by a context manager. It’s commonly used for file operations. It ensures resources like files are properly closed.
- What are Python comprehensions?
Comprehensions are a compact way to create lists, sets, or dictionaries. They are more readable and faster than traditional loops. Example: [x*x for x in range(5)].
- What is the purpose of assert in Python?
assert is used to test conditions that should always be true. If the condition is false, it raises an AssertionError. It’s mostly used in testing and debugging.
- What is a frozen set in Python?
A frozenset is an immutable version of a set. It can’t be modified after creation. It can be used as a dictionary key or set element.
- What is a byte object in Python?
A byte object represents a sequence of bytes. It’s defined using b’…’ syntax. Useful in binary data handling, like files or network communication.
- How do you convert a string to a list in Python?
You can use list(string) to break the string into characters or use split() to break it by spaces. It depends on how you want to split it. Both are useful for text manipulation.
- How do you sort a dictionary by value?
Use sorted(dict.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]). It returns a sorted list of tuples. You can convert it back to a dictionary if needed.
- What is recursion in Python?
Recursion is when a function calls itself. It’s useful for problems like factorial, Fibonacci, or tree traversal. Make sure to include a base case to stop recursion.
- What is the default return value of a function that doesn’t return anything?
If a function doesn’t explicitly return anything, it returns None by default. This is Python’s way of indicating “no value.” You can still call the function for its side effects.
- What are Python modules?
A module is a file containing Python code that can be imported and reused. It can have functions, classes, and variables. You can import it using import module_name.
- How do you install third-party packages in Python?
Use the command pip install package_name. Pip is the Python package manager. Make sure pip is installed and updated.
- What is the difference between compile() and exec()?
compile() converts source code to bytecode, while exec() runs dynamically created Python code. Use them for advanced scripting or dynamic execution. They are rarely used in beginner scripts.
- What is duck typing in Python?
Duck typing means the type or class of an object is less important than the methods it defines. “If it walks like a duck and quacks like a duck, it’s a duck.” Python relies on behavior over type.
- What is the difference between mutable and immutable types?
Mutable types can change their values (like lists), while immutable types cannot (like strings, tuples). Changing immutable types creates new objects. It affects memory and performance.
- What is slicing in Python?
Slicing allows you to get a subset of a list, string, or tuple using [start:stop:step] syntax. It’s flexible and readable. It helps with data extraction and manipulation.
- What is the use of id() in Python?
id() returns the unique identity of an object. It’s like the object’s memory address. Useful to check if two variables point to the same object.
- What is the difference between pop() and remove() in lists?
pop() removes an item by index and returns it, while remove() deletes the first matching value. pop() can work without arguments to remove the last item. remove() doesn’t return the removed item.
- How do you copy a list in Python?
You can use slicing list[:], the copy() method, or list() constructor. All create a shallow copy. For nested lists, use deepcopy() from the copy module.
- What is the purpose of setdefault() in dictionaries?
setdefault() returns the value for a key if it exists, or sets it to a default value if it doesn’t. It’s useful for initializing dictionary entries. It avoids key errors.
- What is the dir() function in Python?
The dir() function returns all the attributes and methods of an object. It helps inspect what functions or variables are associated with that object. It’s useful for debugging and exploration.
- What is the difference between locals() and globals()?
locals() returns a dictionary of the current local symbol table, while globals() returns the global one. They’re used to access variable scope dynamically. Useful in functions and modules.
- What is the use of help() in Python?
help() opens the built-in help system in Python. It provides documentation for modules, functions, classes, or keywords. It’s useful for quick reference.
- What is the use of eval() in Python?
eval() runs a string as a Python expression and returns the result. It’s powerful but should be used with caution due to security risks. Common in calculators and scripting tools.
- What is the map() function used for?
map() applies a function to each item of an iterable and returns a map object. You can convert it to a list. It’s useful for transforming data.
- What is the filter() function in Python?
filter() filters elements of an iterable based on a function that returns True or False. It returns a filter object. Use it to remove unwanted items from a sequence.
- What does any() do in Python?
any() returns True if at least one element in an iterable is true. If all elements are false or empty, it returns False. It’s useful in condition checking.
- What does all() do in Python?
all() returns True only if all elements in an iterable are true. It returns False if any element is false. Often used in data validation.
- What is the use of abs() function?
abs() returns the absolute value of a number, removing any negative sign. It works with integers and floats. Helpful in math operations.
- What is the purpose of round() in Python?
round() rounds a number to the nearest integer or to a specified number of decimal places. It’s commonly used in formatting or calculations. Example: round(3.14159, 2) gives 3.14.
- What is frozenset() used for?
frozenset() creates an immutable set. Once created, you cannot add or remove elements. It’s useful when you need a set that must remain unchanged.
- What does reversed() do?
reversed() returns a reversed iterator over a sequence. It doesn’t modify the original object. Convert it to a list or string to see the output.
- What is the use of isinstance()?
isinstance() checks if an object is an instance of a specific class or type. It returns True or False. It’s useful for type checking before operations.
- What is a memory view in Python?
A memory view is an object that exposes the memory of other binary objects like bytes or bytearray. It helps avoid copying large data. It’s efficient for binary processing.
- What are keyword arguments?
Keyword arguments are passed to functions by explicitly specifying parameter names. Example: func(name=”John”). It improves readability and avoids order dependency.
- What are positional arguments?
Positional arguments are passed based on their position in the function call. Example: func(“John”, 25). The order must match the function definition.
- What is variable shadowing?
Variable shadowing happens when a local variable has the same name as a global variable. The local variable hides the global one. It can lead to confusion or bugs.
- What is the use of nonlocal keyword?
nonlocal is used inside nested functions to modify a variable in the enclosing (non-global) scope. Without it, you can’t change that outer variable. It’s similar to global, but for nested functions.
- What is the use of global keyword?
global allows you to modify a global variable inside a function. Without it, assigning a variable creates a local one. It’s used when you need to keep shared state.
- What is the purpose of del in Python?
del is used to delete variables, list items, or dictionary keys. It removes references to objects. After deletion, the object may be garbage collected.
- What is a traceback in Python?
A traceback is a report showing the call stack when an error occurs. It helps identify where the error happened. It includes file names, line numbers, and error types.
- What is the use of try-except block?
The try-except block handles exceptions during runtime. Code in the try block is executed, and if an error occurs, the except block runs. It prevents program crashes.
- What is exception handling in Python?
Exception handling is the process of managing errors gracefully using try, except, finally, and else. It keeps the program running even after encountering errors. It’s essential for robust code.
- What is a traceback object?
A traceback object contains information about the call stack at the point an exception was raised. It is used in debugging tools. You can access it via sys.exc_info().
- What is Python used for?
Python is used for web development, data science, automation, scripting, AI, and more. It’s known for its simplicity and versatility. That’s why it’s popular among beginners and professionals.



